Overview

Flat feet are a common problem. They can easily be identified by even non-trained individuals as the appearance is quite clear. On the inside of the foot should be a nice curvature which raises the inner foot up off the floor. If the foot touches the floor consistently from heel to toes then the foot is considered flat.
Causes
As discussed above, many health conditions can create a painful flatfoot. Damage to the posterior tibial tendon is the most common cause of AAFD. The posterior tibial tendon is one of the most important tendons of the leg. It starts at a muscle in the calf, travels down the inside of the lower leg and attaches to the bones on the inside of the foot. The main function of this tendon is to hold up the arch and support your foot when you walk. If the tendon becomes inflamed or torn, the arch will slowly collapse. Women and people over 40 are more likely to develop problems with the posterior tibial tendon. Other risk factors include obesity, diabetes, and hypertension. Having flat feet since childhood increases the risk of developing a tear in the posterior tibial tendon. In addition, people who are involved in high impact sports, such as basketball, tennis, or soccer, may have tears of the tendon from repetitive use.
Symptoms
Flat feet can cause a myriad of symptoms, from experiencing pain in the foot, heels, arch, calves, the shin, the knee, the hip and into the lower back due to overworking of the hip flexors or they may find it hard to stand on tip toes.
Diagnosis
Many medical professionals can diagnose a flat foot by examining the patient standing or just looking at them. On going up onto tip toe the deformity will correct when this is a flexible flat foot in a child with lax joints. Such correction is not seen in the adult with a rigid flat foot. An easy and traditional home diagnosis is the "wet footprint" test, performed by wetting the feet in water and then standing on a smooth, level surface such as smooth concrete or thin cardboard or heavy paper. Usually, the more the sole of the foot that makes contact (leaves a footprint), the flatter the foot. In more extreme cases, known as a kinked flatfoot, the entire inner edge of the footprint may actually bulge outward, where in a normal to high arch this part of the sole of the foot does not make contact with the ground at all.
high arch feet
Non Surgical Treatment
In rare cases, surgery may be needed if a child has flat feet caused by a problem they're born with (a congenital abnormality). The foot may need to be straightened or the bones may need to be separated if they're fused together. Painkillers and insoles are the first treatment options for flat feet that are caused by a joint problem, such as arthritis or a torn tendon. However, surgery may be recommended if the injury or condition is severely affecting your feet. Where flat feet are caused by a condition that affects the nervous system, special shoes, insoles, or supportive foot or leg braces may be needed. Again, in severe cases, an operation may be needed to straighten the feet.
Surgical Treatment

Rarely does the physician use surgery to correct a foot that is congenitally flat, which typically does not cause pain. If the patient has a fallen arch that is painful, though, the foot and ankle physicians at Midwest Orthopaedics at Rush may perform surgery to reconstruct the tendon and "lift up" the fallen arch. This requires a combination of tendon re-routing procedures, ligament repairs, and bone cutting or fusion procedures.
Prevention
Sit up straight in a chair with your feet flat on the ground. Scrunch up the toes of one foot as if you are trying to grab hold of the floor then use your toes to drag your foot a small distance forwards. Do this a couple of times on each foot, but don?t use your leg muscles to push your foot forward -- the movement should come solely from the muscles in your feet. Sit in a chair and place a cleaning cloth, towel or small ball on the floor at your feet. Use the toes of one foot to grasp the object and lift it off the floor. This action will require you to clench your toes and contract your arch. Once you have lifted the object a little way off the floor, try to throw it in the air and catch it by stretching your toes and arch out and upwards. Repeat the exercise several times on both feet. Sit on the floor with your legs straight out in front of you then bend your knees out to either side and place the soles of your feet together so your legs form a diamond. Hold on to your ankles and, keeping your heels together at all times, separate your feet so your toes point out to either side. Open and close your feet in this way several times, making sure your little toes stay in contact with the floor throughout the exercise. Starting in the same position, try separating your heels, keeping your toes together at all times.
After Care
Patients may go home the day of surgery or they may require an overnight hospital stay. The leg will be placed in a splint or cast and should be kept elevated for the first two weeks. At that point, sutures are removed. A new cast or a removable boot is then placed. It is important that patients do not put any weight on the corrected foot for six to eight weeks following the operation. Patients may begin bearing weight at eight weeks and usually progress to full weightbearing by 10 to 12 weeks. For some patients, weightbearing requires additional time. After 12 weeks, patients commonly can transition to wearing a shoe. Inserts and ankle braces are often used. Physical therapy may be recommended. There are complications that relate to surgery in general. These include the risks associated with anesthesia, infection, damage to nerves and blood vessels, and bleeding or blood clots. Complications following flatfoot surgery may include wound breakdown or nonunion (incomplete healing of the bones). These complications often can be prevented with proper wound care and rehabilitation. Occasionally, patients may notice some discomfort due to prominent hardware. Removal of hardware can be done at a later time if this is an issue. The overall complication rates for flatfoot surgery are low.

Flat feet are a common problem. They can easily be identified by even non-trained individuals as the appearance is quite clear. On the inside of the foot should be a nice curvature which raises the inner foot up off the floor. If the foot touches the floor consistently from heel to toes then the foot is considered flat.
Causes
As discussed above, many health conditions can create a painful flatfoot. Damage to the posterior tibial tendon is the most common cause of AAFD. The posterior tibial tendon is one of the most important tendons of the leg. It starts at a muscle in the calf, travels down the inside of the lower leg and attaches to the bones on the inside of the foot. The main function of this tendon is to hold up the arch and support your foot when you walk. If the tendon becomes inflamed or torn, the arch will slowly collapse. Women and people over 40 are more likely to develop problems with the posterior tibial tendon. Other risk factors include obesity, diabetes, and hypertension. Having flat feet since childhood increases the risk of developing a tear in the posterior tibial tendon. In addition, people who are involved in high impact sports, such as basketball, tennis, or soccer, may have tears of the tendon from repetitive use.
Symptoms
Flat feet can cause a myriad of symptoms, from experiencing pain in the foot, heels, arch, calves, the shin, the knee, the hip and into the lower back due to overworking of the hip flexors or they may find it hard to stand on tip toes.
Diagnosis
Many medical professionals can diagnose a flat foot by examining the patient standing or just looking at them. On going up onto tip toe the deformity will correct when this is a flexible flat foot in a child with lax joints. Such correction is not seen in the adult with a rigid flat foot. An easy and traditional home diagnosis is the "wet footprint" test, performed by wetting the feet in water and then standing on a smooth, level surface such as smooth concrete or thin cardboard or heavy paper. Usually, the more the sole of the foot that makes contact (leaves a footprint), the flatter the foot. In more extreme cases, known as a kinked flatfoot, the entire inner edge of the footprint may actually bulge outward, where in a normal to high arch this part of the sole of the foot does not make contact with the ground at all.
high arch feet
Non Surgical Treatment
In rare cases, surgery may be needed if a child has flat feet caused by a problem they're born with (a congenital abnormality). The foot may need to be straightened or the bones may need to be separated if they're fused together. Painkillers and insoles are the first treatment options for flat feet that are caused by a joint problem, such as arthritis or a torn tendon. However, surgery may be recommended if the injury or condition is severely affecting your feet. Where flat feet are caused by a condition that affects the nervous system, special shoes, insoles, or supportive foot or leg braces may be needed. Again, in severe cases, an operation may be needed to straighten the feet.
Surgical Treatment

Rarely does the physician use surgery to correct a foot that is congenitally flat, which typically does not cause pain. If the patient has a fallen arch that is painful, though, the foot and ankle physicians at Midwest Orthopaedics at Rush may perform surgery to reconstruct the tendon and "lift up" the fallen arch. This requires a combination of tendon re-routing procedures, ligament repairs, and bone cutting or fusion procedures.
Prevention
Sit up straight in a chair with your feet flat on the ground. Scrunch up the toes of one foot as if you are trying to grab hold of the floor then use your toes to drag your foot a small distance forwards. Do this a couple of times on each foot, but don?t use your leg muscles to push your foot forward -- the movement should come solely from the muscles in your feet. Sit in a chair and place a cleaning cloth, towel or small ball on the floor at your feet. Use the toes of one foot to grasp the object and lift it off the floor. This action will require you to clench your toes and contract your arch. Once you have lifted the object a little way off the floor, try to throw it in the air and catch it by stretching your toes and arch out and upwards. Repeat the exercise several times on both feet. Sit on the floor with your legs straight out in front of you then bend your knees out to either side and place the soles of your feet together so your legs form a diamond. Hold on to your ankles and, keeping your heels together at all times, separate your feet so your toes point out to either side. Open and close your feet in this way several times, making sure your little toes stay in contact with the floor throughout the exercise. Starting in the same position, try separating your heels, keeping your toes together at all times.
After Care
Patients may go home the day of surgery or they may require an overnight hospital stay. The leg will be placed in a splint or cast and should be kept elevated for the first two weeks. At that point, sutures are removed. A new cast or a removable boot is then placed. It is important that patients do not put any weight on the corrected foot for six to eight weeks following the operation. Patients may begin bearing weight at eight weeks and usually progress to full weightbearing by 10 to 12 weeks. For some patients, weightbearing requires additional time. After 12 weeks, patients commonly can transition to wearing a shoe. Inserts and ankle braces are often used. Physical therapy may be recommended. There are complications that relate to surgery in general. These include the risks associated with anesthesia, infection, damage to nerves and blood vessels, and bleeding or blood clots. Complications following flatfoot surgery may include wound breakdown or nonunion (incomplete healing of the bones). These complications often can be prevented with proper wound care and rehabilitation. Occasionally, patients may notice some discomfort due to prominent hardware. Removal of hardware can be done at a later time if this is an issue. The overall complication rates for flatfoot surgery are low.



 This is a painful condition affecting a small nerve in the foot. It occurs when the five long bones that run the length of the foot get pushed together, pinching the nerve in between. This friction on the nerve causes it to thicken and inflame causing pain. The condition gets its name from an American surgeon, George Morton.
This is a painful condition affecting a small nerve in the foot. It occurs when the five long bones that run the length of the foot get pushed together, pinching the nerve in between. This friction on the nerve causes it to thicken and inflame causing pain. The condition gets its name from an American surgeon, George Morton.
 A bunion is a ?bump? on the joint at the base of the big toe-the metatarsophalangeal (MTP) joint-that forms when the bone or tissue at the big toe joint moves out of place. The toe is forced to bend toward the others, causing an often painful lump of bone on the foot. Because this joint carries a lot of the body's weight while walking, bunions can cause extreme pain if left untreated. The MTP joint itself may become stiff and sore, making even the wearing of shoes difficult or impossible. A bunion-from the Latin "bunio," meaning enlargement, can also occur on the outside of the foot along the little toe, where it is called a "bunionette" or "tailor's bunion".
A bunion is a ?bump? on the joint at the base of the big toe-the metatarsophalangeal (MTP) joint-that forms when the bone or tissue at the big toe joint moves out of place. The toe is forced to bend toward the others, causing an often painful lump of bone on the foot. Because this joint carries a lot of the body's weight while walking, bunions can cause extreme pain if left untreated. The MTP joint itself may become stiff and sore, making even the wearing of shoes difficult or impossible. A bunion-from the Latin "bunio," meaning enlargement, can also occur on the outside of the foot along the little toe, where it is called a "bunionette" or "tailor's bunion".


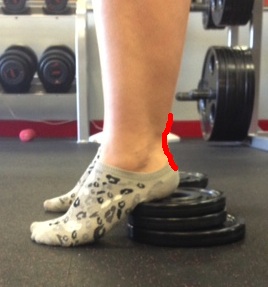 Achilles tendon is a strong fibrous cord present behind the ankle that connects the calf muscles to heel bone. It is used when you walk, run and jump. When the Achilles tendon becomes thin, weak, or if it is not used, it may be susceptible to injury or damage. Achilles tendon rupture occurs most often in middle-aged athlete participating in sports that involve running, pivoting, and jumping. Recreational sports that may cause Achilles rupture include tennis, racquetball, basketball, and badminton.
Achilles tendon is a strong fibrous cord present behind the ankle that connects the calf muscles to heel bone. It is used when you walk, run and jump. When the Achilles tendon becomes thin, weak, or if it is not used, it may be susceptible to injury or damage. Achilles tendon rupture occurs most often in middle-aged athlete participating in sports that involve running, pivoting, and jumping. Recreational sports that may cause Achilles rupture include tennis, racquetball, basketball, and badminton.




